Introduction
The abuse of antibiotic growth promoters (AGPs) in feed has led to drug resistance and ecological damage would threaten human health eventually. Natural plants have become a hotspot in the research and application of substituting AGPs because of their advantages of safety, efficiency, and availability (Songchang et.al.2021).
Necrotic enteritis (NE), an enterotoxemic disease in poultry, is primarily caused by Clostridium perfringens. The restriction or ban of in-feed antibiotics in regions such as the European Union and China has contributed to a resurgence of NE cases (Shojadoost et.al.2012). The disease is particularly severe in young broilers, with acute mortality rates reaching up to 50%. NE is associated with a significant upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, contributing to systemic immune activation (Lee et.al.2011). As inflammation is metabolically demanding, immune challenges can increase the resting metabolic rate of animals by 8–27%, thereby diverting energy from growth and maintenance processes (Martin et.al.2003).
Inflammation in poultry reduces feed intake, disrupts intestinal morphology, limits nutrient absorption, and redirects energy to immune responses, collectively impairing growth and causing intestinal damage and economic losses (Klasing et.al.1987). Necrotic enteritis (NE) aggravates these effects by inducing gut microbiota dysbiosis, marked by reduced diversity, instability, and enrichment of pro-inflammatory bacteria, which compromise intestinal homeostasis and enhance pathogen persistence (Satokari et.al.2015).
Macleaya cordata is a perennial herb widely distributed in southern China and traditionally used in herbal medicine. Its extract (MCE), which contains bioactive alkaloids such as sanguinarine and chelerythrine, was approved as a feed additive in the EU in 2004. Sanguinarine, the major active compound, has demonstrated antitumor (Fu.et.al.2018), immunomodulatory (Kumar et.al.2014), antibacterial (Hamoud et.al.2014), anti-inflammatory (Xue et.al.2017), and insecticidal (Li et.al.2017) properties.
Several investigators have reported that MCE diets could ameliorate production performance, improve gut health and body immunity, and promote growth (Bojjireddy et al., 2013; Khadem et al., 2014). Besides, sanguinarine is the major active ingredient of M. cordata, which has been found to have anti-inflammatory activity (Niu et al.2012), inhibit the activation of NF-κB, and regulate inflammatory response (Wullaert et. al.2011). Gradually, it evoked attention as a substitute of antibiotics (Kim et al.2012). Although sanguinarine is poisonous, an average daily oral dose of alkaloids of up to 5 mg/kg animal body weight has been proven safe (Kosina et al., 2004).
MCE has been reported to modulate intestinal microbiota, particularly in the upper gastrointestinal tract. It promotes beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus, inhibits Escherichia coli colonization, and stimulates amino acid, vitamin, and bile acid biosynthetic pathways, while minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance gene accumulation (Huang et.al.2018).
While MCE’s beneficial effects on broiler performance, intestinal integrity, and inflammation have been demonstrated, its impact on humoral immune function and microbiota-mediated amelioration of NE remains insufficiently characterized (Bui et.al.2015).
Objective of Study-
To evaluate the effect of PHYTOGIC on the performance of commercial broilers reared on deep litter under field conditions.
Materials and Methods
Experimental Design and Management
The trial was conducted at Harsh Broiler House using Vencobb 430 straight run chicks (not sexed at hatchery) in three treatments of around 12000 birds in each treatment. A total of 36000 birds were considered for trial purpose. Feed Formulation used was same for all treatment groups except in T2 where PHYTOGIC was added at 150 gm per ton feed respectively in all stages. (Table 1.) In the study, the energy level was equivalent to the standard requirements of broilers recommended in the Vecobb 430. The trial was carried out over a period of 42 days. The birds were fed ad lib feed and water was available all the times. Care was taken to provide good conditions by adopting strict biosecurity measures. The housing and vaccination procedures were same in both groups.
Table 1. Composition of basal diet for broiler chicks in control group for 3 phases.
| Broiler Feed Formulation (Control) | |||
| Raw Materials | Prestarter | Starter | Finisher |
| Maize | 625.15 | 652.75 | 686.65 |
| HiPro Soya | 335 | 300 | 260 |
| Soya Crude Oil | 6 | 14 | 23 |
| Limestone Powder | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8 |
| Dicalcium Phosphate | 10 | 10 | 8 |
| L Lysine HCI | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.3 |
| DL Methionine | 3.3 | 3 | 2.7 |
| L Threonine | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Salt | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Soda Bi Carb | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Choline Chloride 60% | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Organic TM | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Broiler Vitamin Premix | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Coccidiostat | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| AGP | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| NSP Enzyme | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Phytase 5000 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Feed Acidifier | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Toxin Binder | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
*The figures are in Kilograms.
The premix provided the following per kilogram of the diet: vitamin A, 6000 IU; vitamin D3, 2500 IU; vitamin B1, 1.75 mg; vitamin B2, 5.5 mg; vitamin B6, 4 mg; vitamin B12, 0.18 mg; vitamin E, 25 mg; vitamin K3, 2.25 mg; Cu, 7.5 mg; Mn, 60 mg; Fe, 75 mg; Zn, 60 mg; Se, 0.15 mg; biotin, 0.14 mg; NaCl, 3.7 g; folic acid, 0.8 mg; pantothenic acid, 12 mg; phytase, 400 U; nicotinic acid, 34 mg; chloride, 350 mg. *Nutrient levels were all calculated values.
Treatment Details-
T1: Control group fed basal diet
T2: Control group fed basal diet + PHYTOGIC @150 g PMT
Parameters Studied-
- Body Weight gain was recorded weekly
- Feed Consumption recorded daily and leftover feed was adjusted in the other day quota to know actual intake.
- Mortality was recorded daily
- EEF calculated post harvesting of the flock
- FCR was calculated every week and post harvesting of the flock.
Results:
Effect of Supplementation of Phytogic on body growth performance parameters like Body Weights, Feed Consumption, FCR and Average Daily gain of Control and Treatment Groups
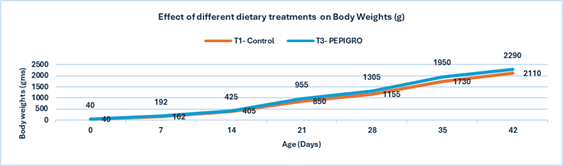
Fig.1. Effect of different dietary treatments on Body Weights (g)
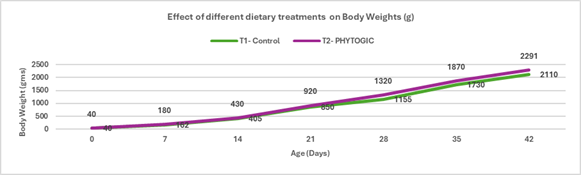
Conclusion:Broilers in the T2 – PHYTOGIC group fed at 150g/ton of feed achieved higher final body weights (2291 g) compared to the T1 – Control group (2110 g), showing an 8.22% improvement. This indicates that PHYTOGIC supplementation effectively enhances growth performance in broilers.
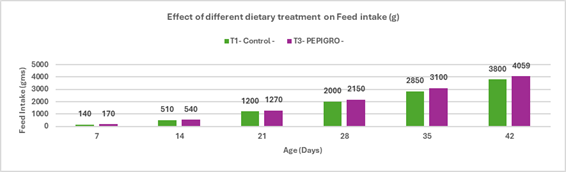
Fig.2. Effect of different dietary treatments on Feed Intake (g)
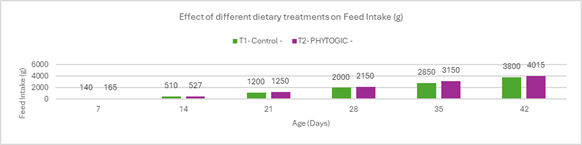
Conclusion:Broilers in the T2 – PHYTOGIC group fed at 150g/ton of feed consumed more feed (4015 g) compared to the T1 – Control group (3800 g), showing a 5.50% increase in feed intake. This suggests that PHYTOGIC supplementation may enhance feed consumption in broilers.
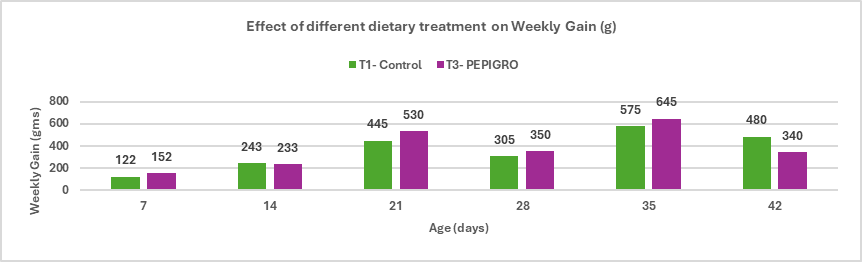
Fig.3. Effect of different dietary treatments on Weekly Gain (g)
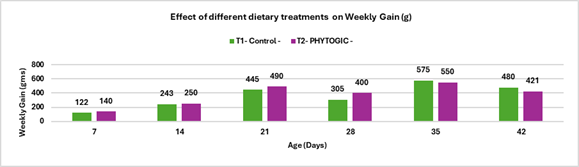
Conclusion: The average weekly percentage difference in weight gain between T2 – PHYTOGIC fed at 150g/ton of feed and T1 – Control was -3.84%, indicating that, overall, PHYTOGIC supplementation did not improve weekly weight gain in broilers and was slightly less effective than the control in this trial.
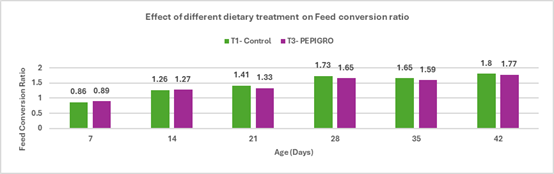
Fig.4. Effect of different dietary treatments on Feed Conversion Ratio
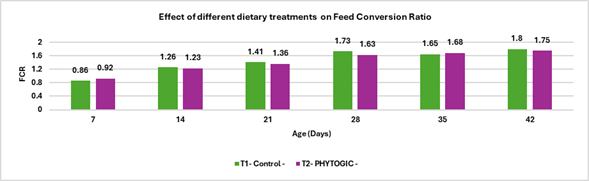
Conclusion:Broilers in the T2 – PHYTOGIC group fed at 150g/ton of feed showed an improved feed conversion ratio (1.75) compared to the T1 – Control group (1.80), with a 2.81% improvement. This suggests that PHYTOGIC supplementation enhances feed efficiency in broilers, allowing for better weight gain per unit of feed consumed.
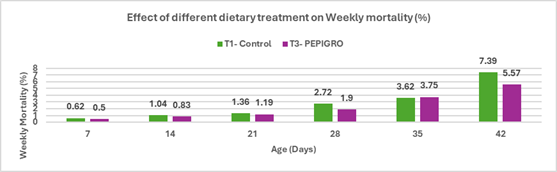
Fig.5. Effect of different dietary treatments on Weekly Mortality (%)
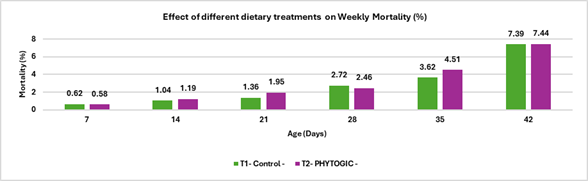
Conclusion:The mortality rate in the T2 – PHYTOGIC group fed at 150g/ton of feed was (7.44%) slightly higher than the T1 – Control group (7.39%), with a 0.27% difference. This minimal variation indicates that PHYTOGIC supplementation had no significant effect on broiler mortality under the conditions of this study.
Table 2. Summary of the Report-
| Parameters | T1- Control | T2- PHYTOGIC | % Difference |
| Body Weight (g) | 2110 | 2291 | 8.22 |
| Feed Intake (g) | 3800 | 4015 | 5.50 |
| FCR | 1.80 | 1.75 | 2.81 |
| CFCR | 1.77 | 1.67 | 5.81 |
| Mortality (%) | 7.39 | 7.44 | 0.27 |
Conclusion-
- The trial was conducted in the extreme heat season where average temperature in the surrounding was around 42-45 degree Celsius.
- The T2 (PHYTOGIC) groups showed overall improved performance compared to the T1 (Control) group.
- Specifically, the body weight of T2 (PHYTOGIC) was 8.22% higher than T1 (Control), indicating better growth.
- Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) and Corrected FCR (CFCR) were both lower in T2 (PHYTOGIC) by 2.81% and 5.81%, respectively, demonstrating more efficient feed utilization in the T2 (PHYTOGIC) group than T1 (Control).
- Mortality rates were nearly identical between the two groups, indicating that the supplement did not adversely affect survival.
Overall, PHYTOGIC supplementation resulted in better growth performance and feed efficiency compared to the control with no significant impact on mortality.
References:
Bojjireddy N., Sinha R.K., Panda D., Subrahmanyam G. Sanguinarine suppresses IgE induced inflammatory responses through inhibition of type II PtdIns 47kinase(s) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013;537:192–197. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.07.017.
Bui TP, Ritari J, Boeren S, de Waard P, Plugge CM, de Vos WM. Production of butyrate from lysine and the amadori product fructoselysine by a human gut commensal. Nat Commun. 2015;6:10062.
Fu C, Guan G, Wang H. The anticancer effect of sanguinarine: A review. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:2760–4.
Hamoud R, Reichling J, Wink M. Synergistic antimicrobial activity of combinations of sanguinarine and edta with vancomycin against multidrug resistant bacteria. Drug Metab Lett. 2014;8:119–28.
Huang P, Zhang Y, Xiao K, Jiang F, Wang H, Tang D, et al. The chicken gut metagenome and the modulatory effects of plant-derived benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Microbiome. 2018;6:211.
Khadem A., Soler L., Everaert N., Niewold T.A. Growth promotion in broilers by both oxytetracycline and Macleaya cordata extract is based on their anti-inflammatory propertiese. Br. J. Nutr. 2014;112:1110–1118. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514001871.
Kim J.C., Hansen C.F., Mullan B.P., Pluske J.R. Nutrition and pathology of weaner pigs: Nutritional strategies to support barrier function in the gastrointestinal tract. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012;173:3–16.
Klasing KC, Laurin DE, Peng RK, Fry DM. Immunologically mediated growth depression in chicks: Influence of feed intake, corticosterone and interleukin-1. J Nutr. 1987;117:1629–37.
Kosina P., Walterova D., Ulrichova J., Lichnovsky V., Stiborova M., Rydlova H., Vicar J., Krecman V., Brabec M.J., Simanek V. Sanguinarine and chelerythrine: assessment of safety on pigs in ninety days feeding experiment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004;42:85–91. doi:
Kumar GS, Hazra S. Sanguinarine, a promising anticancer therapeutic: Photochemical and nucleic acid binding properties. RSC Adv. 2014;4:56518–31.
Lee KW, Lillehoj HS, Jeong W, Jeoung HY, An DJ. Avian necrotic enteritis: Experimental models, host immunity, pathogenesis, risk factors, and vaccine development. Poult Sci. 2011;90:1381–90.
Li JY, Huang HB, Pan TX, Wang N, Shi CW, Zhang B, et al. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis in eimeria tenella sporozoites via the generation of reactive oxygen species. Poult Sci. 2022;101:101771.
Martin LB 2nd, Scheuerlein A, Wikelski M. Immune activity elevates energy expenditure of house sparrows: A link between direct and indirect costs? Proc Biol Sci. 2003;270:153–8.
Niu X., Fan T., Li W., Xing W., Huang H. The anti-inflammatory effects of sanguinarine and its modulation of inflammatory mediators from peritoneal macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012;689:262–269. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.05.039.
Satokari R. Contentious host-microbiota relationship in inflammatory bowel disease–can foes become friends again? Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50:34–42.
Shojadoost B, Vince AR, Prescott JF. The successful experimental induction of necrotic enteritis in chickens by clostridium perfringens: A critical review. Vet Res. 2012;43:74.
Songchang Guo, y Jiaxing Lei, y Lulu Liu, y Xiangyong Qu, y Peng Li, y Xu Liu, y Ying Guo, z Qiaoqin Gao, y Fulin Lan, y Bing Xiao, z Changqing He, y and Xiaoyan Zou. Effects of Macleaya cordata extract on laying performance, egg quality, and serum indices in Xuefeng black-bone chicken Songchang . Poultry Science, 2021;100:101031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2021.101031
Wullaert A., Bonnet M.C., Pasparakis M. NF-kappa B in the regulation of epithelial homeostasis and inflammation. Cell Res. 2011;21:146–158. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.175.
Xue GD, Wu SB, Choct M, Pastor A, Steiner T, Swick RA. Impact of a macleaya cordata-derived alkaloid extract on necrotic enteritis in broilers. Poult Sci. 2017;96:3581–5.